Manual rating insurance is a method where rates are determined based on industry standards and classifications, grouping similar risks to ensure fair and consistent premium calculations for policyholders.
1.1 Definition and Basic Concepts
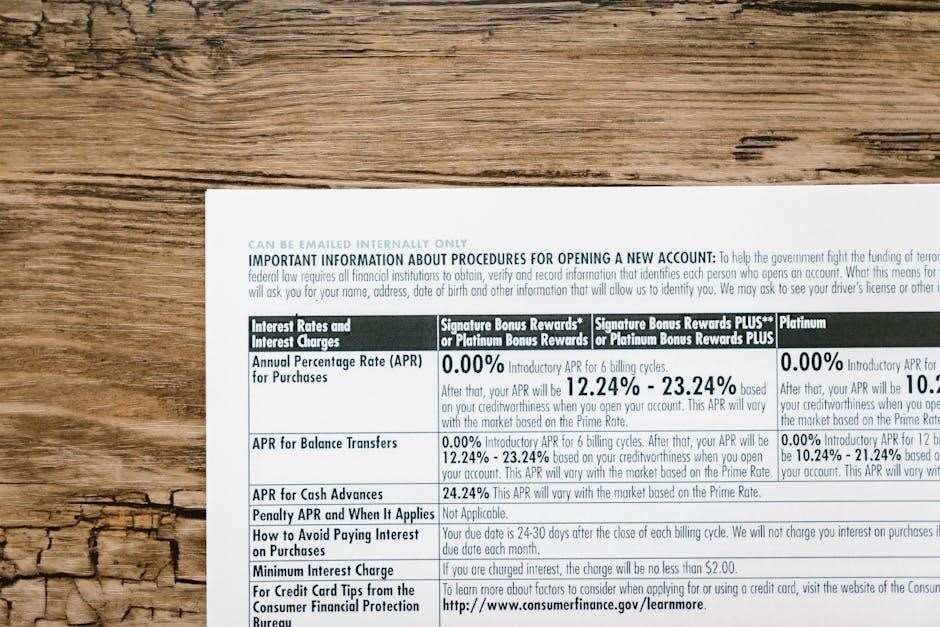
Manual rating insurance refers to a system where insurance premiums are calculated based on standardized rules, classifications, and schedules. It involves grouping employers or risks into categories with similar characteristics to determine fair rates. This method is widely used in workers’ compensation and employers’ liability insurance. The process relies on published manuals that outline rates, rules, and guidelines for underwriters. Supplementary rating information, such as loss costs, policy fees, and minimum premiums, is often included to ensure accurate calculations. The manual rate is typically derived by multiplying the loss cost by a specific factor, such as the Loss Cost Multiplier (LCM). This approach ensures consistency and fairness in pricing, balancing the insurer’s expenses, policyholder risks, and competitive market dynamics. The goal of manual rating is to provide transparent and equitable premiums based on industry standards and historical data.
Key Components of Manual Rating Insurance
Manual rating insurance consists of standardized rules, classifications, and rate schedules. These components help insurers determine fair premiums by grouping similar risks and applying consistent calculation methods.
2.1 Rules and Classification
In manual rating insurance, rules and classification systems are fundamental. These rules guide underwriters in assessing risks and assigning appropriate categories. Classification typically involves grouping businesses or individuals based on industry, occupation, or exposure levels. For example, in workers’ compensation insurance, employers are classified according to their specific industry risks. These classifications are standardized to ensure consistency across policies. The rules outline how factors such as location, type of coverage, and policy limits influence premiums. Supplementary rating information, including loss costs and rating schedules, further refine these classifications. By adhering to these structured guidelines, insurers can maintain fairness and accuracy in premium calculations. This systematic approach ensures that similar risks are treated uniformly, fostering a balanced and equitable insurance marketplace.
2.2 Rate Calculation and Schedules
Rate calculation in manual rating insurance involves determining premiums based on predefined schedules and formulas. Insurers use loss costs, which reflect historical claim data, as a foundation for rate determination. These loss costs are often multiplied by specific factors, such as the insurer’s loss cost multiplier (LCM), to arrive at the manual rate. For instance, the New York State Insurance Fund (NYSIF) calculates manual rates by multiplying loss costs by their LCM. Additionally, rating schedules outline the base rates for different coverage types and risk categories. These schedules are structured to ensure consistency and fairness in pricing. Factors such as policy limits, exposure units, and coverage enhancements are also considered in the calculation process. The final premium is a combination of the manual rate and any applicable adjustments, ensuring that each policy reflects the insured’s specific risk profile and coverage requirements.

How Manual Rating Works
Manual rating assesses risk factors, applies classification codes, and calculates rates using predefined rules and schedules, ensuring fair and consistent pricing based on historical data and industry standards.
3.1 Step-by-Step Process
The manual rating process begins with identifying the insured’s industry and classification code. Insurers then assess risk factors, such as location, business type, and safety measures. Using predefined rating schedules and rules, they calculate the base rate. Adjustments are made based on the insured’s loss history, known as experience rating, and other factors like discounts or surcharges. The final premium is determined by applying these adjustments to the base rate. This systematic approach ensures consistency and fairness in determining insurance premiums, balancing the insurer’s need for profitability with the policyholder’s expectation of reasonable costs. Each step is guided by standardized manuals and guidelines, ensuring transparency and accuracy in the rating process.

Benefits of Manual Rating
Manual rating ensures fair and consistent premiums, balancing profitability for insurers while offering policyholders reasonable costs. It promotes transparency, accountability, and tailored risk assessment, fostering trust and satisfaction for all parties involved.
4.1 Advantages for Insurers and Policyholders
Manual rating offers numerous benefits for both insurers and policyholders. Insurers gain the ability to set fair and consistent premiums, ensuring profitability while maintaining competitiveness. Policyholders benefit from transparent and standardized rates, reducing uncertainties and fostering trust. The system allows insurers to balance their portfolios effectively, managing risks and operational costs. For policyholders, manual rating provides clarity in pricing, enabling informed decision-making. Additionally, it ensures that premiums reflect the actual risk profile, promoting equity among insured parties. This balanced approach strengthens the relationship between insurers and policyholders, fostering long-term partnerships. Overall, manual rating creates a win-win scenario by aligning the interests of both parties through fair, consistent, and transparent pricing practices.

Experience Rating in Manual Insurance
Experience rating in manual insurance adjusts premiums based on an insured’s actual loss history, balancing individual experience with industry data for fair and personalized rate calculations.
5.1 What It Is and How It’s Applied
Experience rating in manual insurance is a method that adjusts premiums based on an insured’s actual loss history compared to industry averages. It balances individual risk with broader data.
This approach ensures fairness by rewarding policyholders with lower losses and adjusting rates for higher-risk entities. Insurers apply it by analyzing historical claims, comparing them to similar risks, and modifying premiums accordingly.
This method is widely used in workers’ compensation and liability insurance, promoting accurate rate setting and encouraging risk management. It aligns premiums with actual risk levels, benefiting both insurers and policyholders.
Future Trends in Manual Rating Insurance
Manual rating insurance is evolving with AI, machine learning, and real-time analytics, improving risk assessment. Challenges include data privacy and adapting to tech advancements.
6.1 Innovations and Challenges
Manual rating insurance is embracing innovations like AI and machine learning to enhance risk assessment and personalize policies. Real-time data integration is improving accuracy, while automation streamlines processes. However, challenges like data privacy concerns and regulatory compliance complicate adoption. Insurers must balance technological advancements with ethical considerations to maintain trust. Additionally, resistance to change and the need for continuous updates to rating manuals pose hurdles. Despite these challenges, the industry is expected to evolve, offering more precise and dynamic pricing models. The integration of predictive analytics could further revolutionize how manual rates are determined, making insurance more responsive to individual risks. As technology advances, insurers must adapt to remain competitive while addressing emerging risks and regulatory demands.
